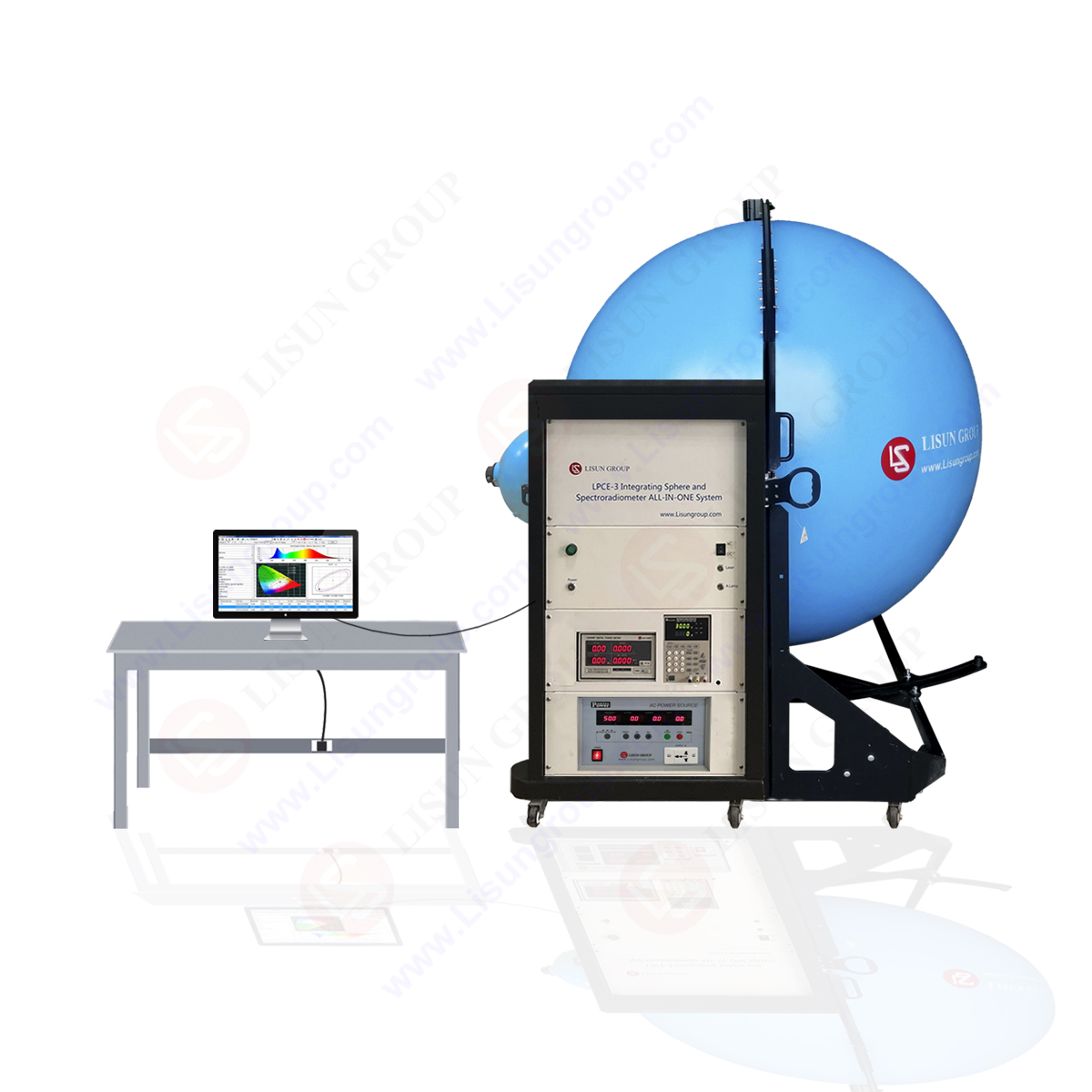
Integrating spheres are essential components of photometry, providing a reliable and accurate way to measure light intensity. By integrating spheres into your photometry system, you can benefit from improved accuracy, repeatability, and flexibility. To learn more about the advantages of integrating spheres in photometry, click here.
Integrating spheres are designed to provide a uniform light source, which is essential for accurate photometry measurements. By using an integrating sphere, you can ensure that the light source is evenly distributed, eliminating any potential errors caused by uneven illumination. Additionally, integrating spheres are highly repeatable, meaning that you can rely on consistent results each time you measure light intensity.
Integrating spheres also offer flexibility in terms of the types of light sources that can be used. By using an integrating sphere, you can measure light intensity from a variety of sources, including LEDs, halogen lamps, and fluorescent lamps. This flexibility allows you to use the same photometry system for a variety of applications.
At LISUN Group, we offer a wide range of integrating spheres for photometry applications. Our integrating spheres are designed to provide reliable and accurate measurements, and are available in a variety of sizes and configurations. To learn more about our integrating spheres, click here.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Photometry is a branch of optics that deals with the measurement of light intensity and its application in various fields. Integrating spheres are an important tool used in photometry to measure the total light output of a source. This article will provide an overview of the benefits of integrating spheres in photometry, including their ability to measure total light output, their ability to measure the spectral distribution of light, and their ability to measure the angular distribution of light. Additionally, this article will discuss the advantages of integrating spheres over other photometric measurement techniques. By understanding the benefits of integrating spheres in photometry, researchers and engineers can make informed decisions when selecting the best photometric measurement technique for their application.
Introduction to Photometry and Integrating Spheres
Photometry and integrating spheres are two important tools used in the field of optical engineering. Photometry is the science of measuring light, while integrating spheres are used to measure the total amount of light emitted from a source. Together, these two tools are used to measure the intensity, color, and other characteristics of light sources.
Photometry is the science of measuring light. It is used to measure the intensity, color, and other characteristics of light sources. Photometers are used to measure the amount of light emitted from a source. These instruments measure the amount of light in terms of luminous flux, which is the total amount of light emitted from a source. Photometers can also measure the color of light, which is important for applications such as color matching and color rendering.
Integrating spheres are used to measure the total amount of light emitted from a source. An integrating sphere is a hollow sphere with a white interior surface. The interior surface is designed to evenly distribute the light from the source, allowing for accurate measurements of the total amount of light emitted. Integrating spheres are used in a variety of applications, including measuring the total luminous flux of a light source, measuring the color of a light source, and measuring the efficiency of a light source.
Photometry and integrating spheres are essential tools for optical engineers. They are used to measure the intensity, color, and other characteristics of light sources. By using these tools, engineers can ensure that light sources are producing the desired amount of light and that the light is of the desired color.
Advantages of Integrating Spheres in Photometry
Integrating spheres are a key component of photometry, a branch of optics that deals with the measurement of light. Integrating spheres are used to measure the total amount of light emitted from a source, as well as the spectral distribution of the light. They are also used to measure the intensity of light from a source, and to compare the intensity of light from different sources.
Integrating spheres are highly efficient at collecting light from a source, as they are designed to absorb and diffuse light evenly. This ensures that the light is evenly distributed throughout the sphere, allowing for accurate measurements of the total amount of light emitted from a source. Additionally, integrating spheres are designed to minimize the amount of light that is reflected back to the source, which helps to reduce errors in the measurements.
Integrating spheres are also useful for measuring the spectral distribution of light from a source. By using a spectrometer, the light from the source can be broken down into its component wavelengths, allowing for the measurement of the intensity of light at each wavelength. This is useful for determining the color of the light, as well as for analyzing the spectral composition of the light.
Integrating spheres are also useful for comparing the intensity of light from different sources. By using a photometer, the intensity of light from each source can be measured and compared. This is useful for determining the relative brightness of different sources, as well as for analyzing the spectral composition of the light from each source.
Overall, integrating spheres are an essential tool for photometry, as they allow for accurate measurements of the total amount of light emitted from a source, as well as the spectral distribution of the light. They are also useful for comparing the intensity of light from different sources, allowing for the analysis of the spectral composition of the light from each source.
Applications of Integrating Spheres in Photometry
Integrating spheres are a type of optical device used in photometry, which is the science of measuring light. They are used to measure the intensity, color, and other characteristics of light sources. Integrating spheres are designed to collect and measure light from a source, and then integrate the light over a large area. This allows for accurate measurements of the light’s intensity, color, and other characteristics.
Integrating spheres are used in a variety of applications, including lighting design, product testing, and medical imaging. In lighting design, integrating spheres are used to measure the intensity and color of light sources, such as LED lights, to ensure that they meet the desired specifications. In product testing, integrating spheres are used to measure the optical properties of products, such as lenses and mirrors, to ensure that they meet the desired specifications. In medical imaging, integrating spheres are used to measure the intensity and color of light sources used in medical imaging systems, such as X-ray and CT scanners.
Integrating spheres are also used in research and development. They are used to measure the optical properties of materials, such as the reflectivity and transmittance of different materials. This allows researchers to develop new materials with specific optical properties. Integrating spheres are also used to measure the optical properties of optical components, such as lenses and mirrors, to ensure that they meet the desired specifications.
Integrating spheres are an essential tool for photometry, as they allow for accurate measurements of the intensity, color, and other characteristics of light sources. They are used in a variety of applications, from lighting design to medical imaging, and are essential for research and development.
Challenges of Integrating Spheres in Photometry
Integrating spheres in photometry can be a challenging process, especially for those who are new to the field. An integrating sphere is a device used to measure the total amount of light emitted from a light source. It is a hollow sphere with a diffuse white interior surface that reflects light in all directions, allowing for the measurement of total light output.
The first challenge of integrating spheres in photometry is the accuracy of the measurements. The sphere must be perfectly round and the interior surface must be perfectly diffuse in order to ensure accurate measurements. If the sphere is not perfectly round or the interior surface is not perfectly diffuse, the measurements will be inaccurate. Additionally, the sphere must be large enough to capture all of the light emitted from the light source. If the sphere is too small, some of the light will be lost and the measurements will be inaccurate.
The second challenge of integrating spheres in photometry is the calibration of the sphere. The sphere must be calibrated to ensure that the measurements are accurate. This involves measuring the reflectance of the interior surface of the sphere and adjusting the calibration to account for any differences in reflectance. Additionally, the sphere must be calibrated to account for any differences in the light source being measured.
The third challenge of integrating spheres in photometry is the setup of the sphere. The sphere must be set up correctly in order to ensure accurate measurements. This includes ensuring that the sphere is level, that the light source is centered in the sphere, and that the sphere is not exposed to any external light sources.
The fourth challenge of integrating spheres in photometry is the analysis of the data. Once the measurements have been taken, the data must be analyzed in order to determine the total light output of the light source. This requires knowledge of photometry and the ability to interpret the data.
Integrating spheres in photometry can be a challenging process, but with the right knowledge and experience, it can be a powerful tool for measuring the total light output of a light source.
Conclusion: Benefits of Integrating Spheres in Photometry
Integrating spheres are an essential tool for photometry, as they provide a reliable and accurate way to measure the intensity of light. Integrating spheres are used to measure the total amount of light emitted from a source, as well as the spectral distribution of the light. This is done by collecting the light from the source and reflecting it off the inner surface of the sphere, which is coated with a diffuse, highly reflective material. The light is then collected by a detector, which measures the intensity of the light.
The main benefit of integrating spheres in photometry is that they provide a uniform light source. This means that the light emitted from the source is evenly distributed across the entire surface of the sphere, allowing for more accurate measurements. Additionally, integrating spheres are able to measure the intensity of light over a wide range of wavelengths, which is important for applications such as colorimetry.
Integrating spheres also provide a high degree of accuracy and repeatability. This is due to the fact that the light is evenly distributed across the surface of the sphere, which eliminates any potential errors caused by uneven illumination. Additionally, integrating spheres are able to measure the intensity of light over a wide range of wavelengths, which is important for applications such as colorimetry.
Integrating spheres are also relatively easy to use and maintain. They require minimal setup and calibration, and they are relatively inexpensive compared to other photometric instruments. Additionally, integrating spheres are relatively compact, making them easy to transport and store.
Overall, integrating spheres provide a reliable and accurate way to measure the intensity of light. They provide a uniform light source, a high degree of accuracy and repeatability, and they are relatively easy to use and maintain. Integrating spheres are an essential tool for photometry, and they are an invaluable asset for any laboratory or research facility.
Conclusion
The integration of spheres in photometry has a wide range of benefits, from improved accuracy and precision to increased efficiency and cost savings. By using spheres, photometric measurements can be made more quickly and accurately, and the data can be used to create more accurate models of light sources. Additionally, the use of spheres can reduce the amount of time and money spent on calibration and testing, making photometry more cost-effective. With the advantages of integrating spheres in photometry, it is clear that this technology can be a valuable asset to any photometric laboratory.

 中文简体
中文简体